Introduction
ADAS, or advanced driver assistance systems, shifted the whole phase of automotive safety and utilization. These systems are no longer extras for the future; they are integral parts that define the current generation’s driving environments. ADAS embraces enhanced technologies like lane-keeping assistance, automatic driving, and emergency braking, among others, to ensure a safe and convenient society. There is potential for specific challenges and business opportunities regarding the implementation and continued use of these systems for service providers. This article presents ADAS systems as discussed from the context of the service providers, detailing their working constituents and underlining the importance of service providers in the ADAS systems’ life cycle.
The Growing Significance of ADAS Systems
The latest market research by Marketsandmarkets reveals that the market for ADAS is on the rise and is predicted to exhibit a CAGR of more than 11% in the coming years to reach nearly 134 billion US dollars by 2030.
From the perspective of service providers, this growth means the necessity of having highly specialized knowledge about ADAS and sound infrastructure to underpin the technology. This knowledge ranges from how the system looks to analyzing the diagnostics, calibration, upgrades, and anything related to updating a car’s software.
Main Features Within ADAS Systems
ADAS systems comprise many interconnected sensors and cameras, processors, and algorithms. Understanding these components is crucial for service providers tasked with maintenance and troubleshooting:
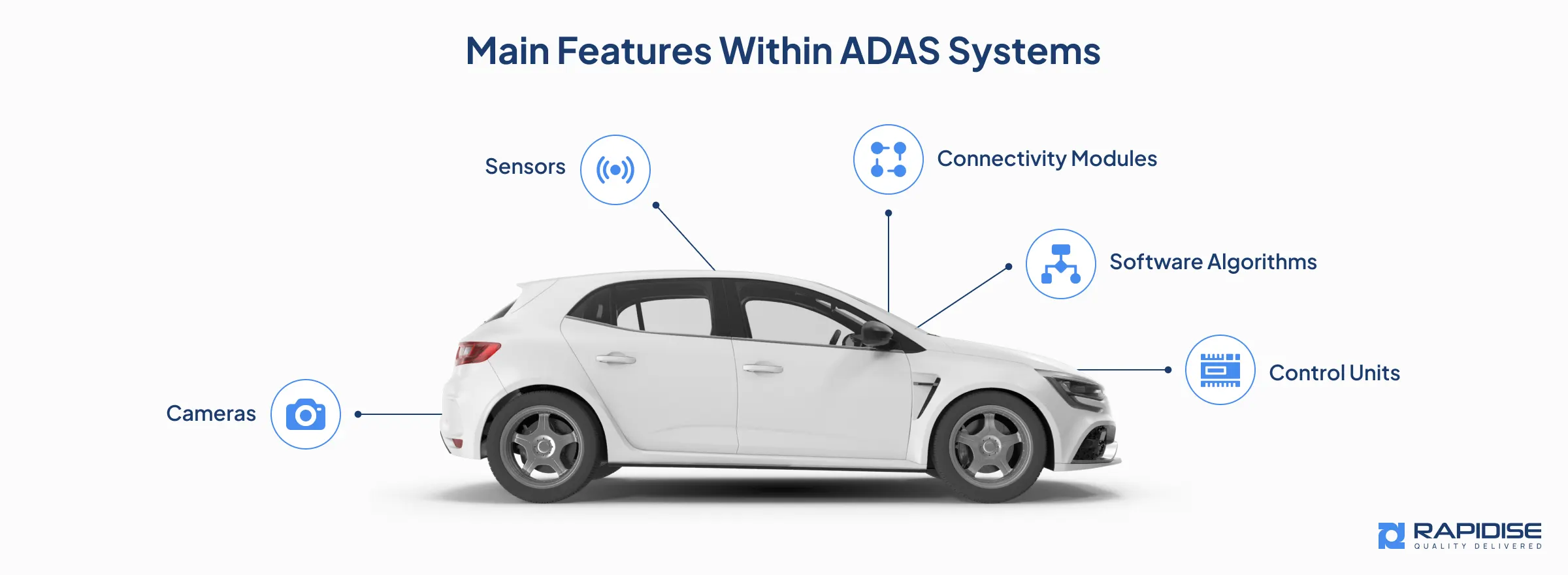
- Sensors: Radar, LiDAR, ultrasonic sensors, and infrared sensors are the key components of an advanced driver assistance system. They identify objects, estimate the distance to these objects and even observe the conditions of the surroundings.
- Cameras: Automakers use high resolution to get visual information for applications such as lane detection, recognizing traffic signs or detecting pedestrians.
- Control Units: Central Computer complexes generally affect decision-making on the sensor information through the ECUs to support the driver or to provide warnings.
- Software Algorithms: Application features, including object recognition, path prediction, and choices, are made possible by sophisticated machine learning algorithms.
- Connectivity Modules: Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) usually allows vehicles to share data with other vehicles and structures.
The Role of Service Providers in ADAS Ecosystems
Service providers play a key role in the proper functioning of ADAS systems during their provision across the auto industry. Their responsibilities span several critical areas:
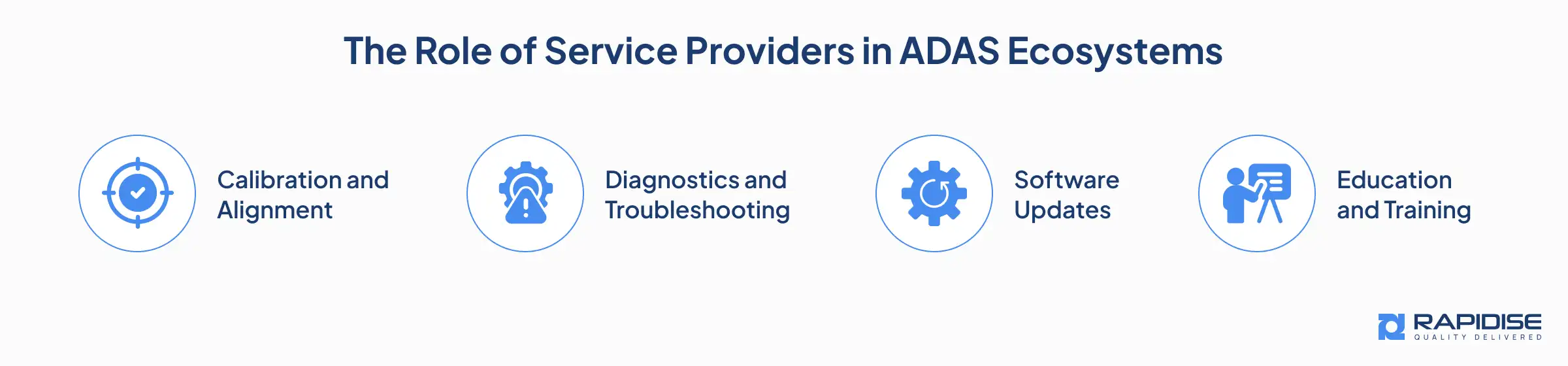
1. Calibration and Alignment
Every component of ADAS has sensors or cameras that need to be calibrated to ensure efficient and proper operation. Misalignment can occur due to minor accidents, changes of tyres, or suspension changes, all of which affect the system. Service providers must:
- Use technical calibration tools.
- Track manufacturer-specific protocols.
- Compliance with the legal requirements must be met.
2. Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
ADAS systems are flexible, but the diagnostics of the problems become more difficult as the systems become more advanced. Service providers must:
- Use sophisticated diagnosis with the capability to communicate with car ECUs.
- Learn to decode errors and understand the messages that sensors convey.
- Fix all kinds of hardware and software problems.
3. Software Updates
ADAS systems depend on the software as the application needs to be updated with new features and security fixes. Service providers must:
- Optimize OTA updates, as they consume an enormous amount of storage.
- Ensure that the vehicle’s current software version—including its accompanying electrical and electronics system—is compatible with the current version of the installed software.
- Tackle issues of cyberspace security.
4. Education and Training
It is, therefore, imperative for service providers to be informed on the prevailing state-of-the-art ADAS systems. Regular training ensures that technicians are proficient in the following:
- Managing the new technologies.
- Adhering to new regulations.
- Informing customers who have purchased cars equipped with ADAS about their functions and, more importantly, their limitations.
Challenges Faced by Service Providers
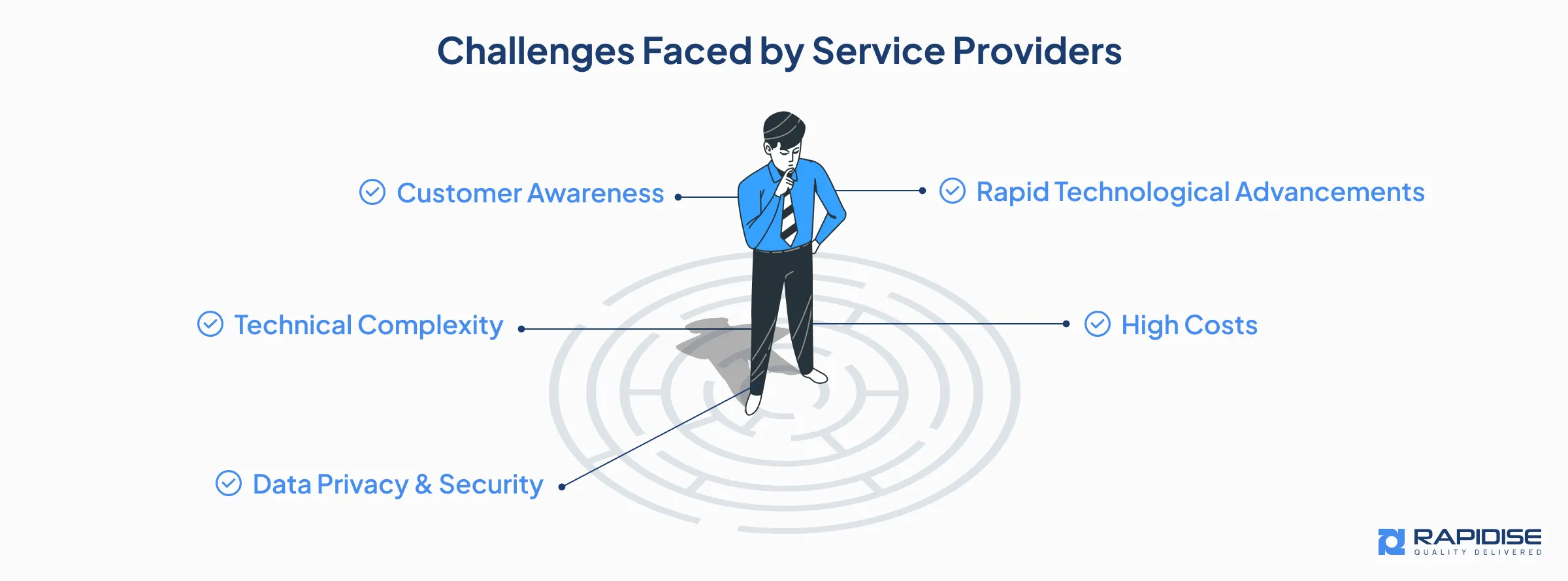
Though ADAS delivers powerful opportunities,but it also poses unique challenges for service providers:
1. Technical Complexity
The architecture of ADAS systems has become complicated and requires specific expertise and equipment that can hardly be utilized at simple service centers.
2. High Costs
For a small or medium service provider, purchasing calibration equipment, diagnostic tools, and training programs beyond an introductory level is expensive.
3. Rapid Technological Advancements
ADAS technology is dynamic, and there is usually a need to learn new concepts at any one time. That is why service providers must be innovative enough to look for what will make them unique enough to capture the market they intend to be in.
4. Data Privacy and Security
With vehicles gaining more extensive data, issues related to data privacy and security threats are being discussed.
5. Customer Awareness
A survey shows that most drivers are not knowledgeable about the capabilities and care of ADAS systems. Ensuring customers understand various issues is a critical task that service providers rarely perform.
Take the First Step Today
Partner with us to unlock the full potential of your ADAS systems. From initial consulting to advanced algorithm optimization on DSP platforms, we provide end-to-end support to bring your product vision to life.
Best Practices for Service Providers
To manage these challenges and maximize the potential of ADAS systems, service providers can adopt the following best practices:
1. Infuse in Advanced Tools and Infrastructure
Ensure your system has cutting-edge calibration and diagnostic tools to manage different ADAS systems.
2. Concentrate on Technician Training
Execute routine training programs to update mechanics on the latest ADAS technologies, measures, and repair protocols.
3. Cooperate with OEMs
Partnering with OEMs can provide a gateway to proprietary tools, software, and technical support.
4. Leverage Digital Solutions
Use digital tools for team workflow organization, remote assessment, and instant customer interactions.
5. Educate Customers
Based on the research findings and conclusions, we offer comprehensive and uncomplicated information about ADAS maintenance and calibration to enhance customers’ satisfaction and confidence in these vehicle features.
The Future of ADAS and Service Providers
The development of ADAS is completely tied to the growth of Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning, connectivity, and Autonomous driving. To the extent that these systems become more commonplace and complex, the function of the service providers will continue to grow. Here are some trends to watch:
1. Integration with Autonomous Vehicles
The advancement of ADAS will form the basis of complete self-driven vehicles, meaning service providers will need to gain knowledge of autonomous driving systems.
2. Enhanced V2X Communication
Enriched V2X technology will require excellent expertise in different aspects, such as the network communication protocol and near real-time information handling.
3. Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance facilitated by AI technology will alert service providers to an impending problem or failure so they can handle it before it triggers extensive damage, thereby cutting down on repair expenses and lost time.
4. Sustainability Initiatives
With the growth of sustainability and the introduction of new eco-friendly systems in the automotive industry, ADAS systems will plug into the green services alternative to help foster environmentally friendly services.
Conclusion
Specific ADAS systems significantly advance car manufacturing and design, improving safety, convenience and efficiency. These systems simultaneously present service providers with certain levels of complexity and flexibility. To this end, service providers must invest further in tools and training programs, familiarize clients with the innovations, and become an essential part of the ADAS environment. The changes being witnessed in the industry require companies to embrace change and adopt the new trends.